Prickly Pear Cactus
Scientific Classification
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| (Unranked): | Angiosperms |
| (Unranked): | Eudicots |
| (Unranked): | Core Eudicots |
| Order: | Caryophyllales |
| Family: | Cactaceae |
| Subfamily: | Opuntioideae |
| Tribe: | Opuntieae |
| Genus: | Opuntiai |
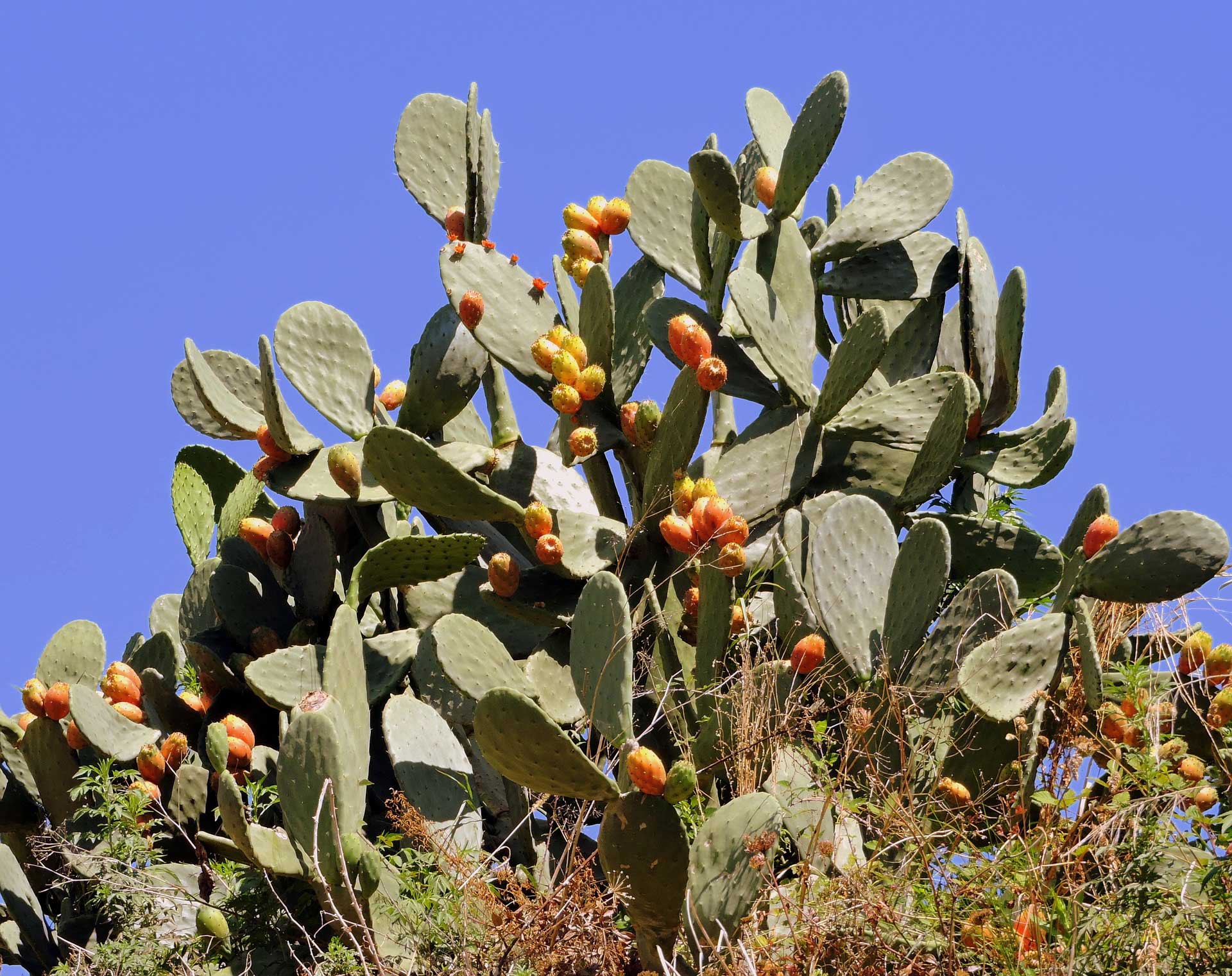
The Prickly pear cactus plant represents many species of the Opuntia genus in the deserts of North America. Prickly pear is also known as Cactus Pear, Tuna or Nopal. All its species have flesh and flat pads which look like large leaves. This plant is easily identified by its flat and broad green pads. Actually, these pads are modified branches and stems which serve many functions such as production of flowers, Photosynthesis and water storage. Its spines are covered with tiny pointed hairs which are known as Glochids. These Glochids are found at the base of the major spines. This plant contains pectin, which is helpful in treating many diseases. This plant has antioxidant properties, so it is part of a healthy diet. The edible parts of this plant are its stems, fruits, leaves and flowers.
History
In the year 1788, the first introduction of the Prickly pear cactus plant was recognized by the earliest colonists in Australia and Governor Phillip.. Having been brought to Sydney from Brazil, this plant grew in New South Wales and Sydney. In 1839, it was rediscovered in the garden of a farmer.
Anatomy
The Prickly Pear cactus plant typically grows with rounded and flat Cladodes, which are also called Platyclades. And they come with two kinds of thorns, fixed and small thorns and large and smooth ones. Hair like prickles are called Glochids, they easily pierce skin and separate from the plant. Many kinds of Prickly pears grow in tangled and dense structures. In the spring season, Its gray-green colored fleshy pads produce large flowers which turn into red, spiny fruits. The fruit of this plant is edible and can also be eaten raw. Its flowers are purple, red and yellow and each flower gives up one fruit. The fruit of this plant grows in a cylindrical shape and is about 2.5 inch long. This fruit is very tasty, rich in nutrients, and also good for health.
Habitat
The prickly pear cactus plant is Native to America, but is has been bought in other parts of the world. In Mexico, species of Prickly pear cactus plant are found in large quantity, especially in Caribbean Island and in western and Central Regions. It is native to areas of the arid western United States and also to lower elevations of the Rocky Mountains. It is also common to sand dunes and dry hills of the East Coast from Florida to Connecticut. It also occurs in isolated areas of Southern Ontario from the Southern great lakes. This plant is native to the Sonora Deserts which is in New Mexico, parts of California and New Arizona. In the British Virgin Islands it is used as a main ingredient of a popular Christmas beverage called “Miss Blyden”.
Growing at Home

Prickly Pear Cactus – Photo by: Yinan Chen
Soil
The prickly pear cactus plant requires coarse and well drained soil. Sand and half mix of soil is also ideal for planting this plant. Once established, it can also survive with just the rain water.
Planting
The prickly pear plant is grown from seeds. The best time to sow seeds is in late spring. On the other hand, cuttings can be planted at any time of year. Growing this plant in colder climate should be done in a container. This plant can be easily propagated from the pads and this method is quite simple and fast.
Watering
The prickly pear plant requires dry soil before watering. It does not require regular irrigation. Watering three times in a month is sufficient. Its root sprouts due to its own moisture. Excessive watering is not good for the plant because it can cause the root rot.
Temperature and Humidity
The prickly pear plant requires a constant room temperature of 60°F. This plant can tolerate moisture and wide range of temperatures.
Care
The prickly pear cactus plant requires full sunlight. It is a drought tolerant plant, frost tolerant, easy to care and requires very low maintenance. This plant can survive in harsh conditions.
Harvesting
The fruit of the prickly pear cactus plant looks so friendly and bashful, with furry dots on it. Actually, these furry dots are zillions of hair like thorns and they steal into skin like the rubble of glass. The Prickly Pear fruit can be eaten after removing its sharp and strong thorns. But to get this fruit, there are few ways. Thick gardening gloves should be worn on the hands. But the gloves will then be covered with dangerous hair, thorns and that will attack next time you touch them. Kitchen forceps are ideal because they keep it at a safe distance and they can also be washed clean without touching the skin.
Pests and Disease
The prickly pear plant is susceptible to Anthracnose disease which is caused by the Colletotrichum species of fungi. Other diseases of this plant are Charcoal Spot and Phyllosticta Pad Spot Disease that cause black lesions on the plant and you will find the pads on the lower part are infected by this disease. Charcoal Spot Disease causes small spotting on the plant. There is no control of this disease. This plant does not attract many pests, but some pests such as mealy bug and scale are the main problems.
Uses
The prickly pear cactus plant is very useful, and its branches which are also called pads are cooked and eaten as a vegetable. These pads and fruits of this plant are rich in soluble fibers and they also help in the treatment of blood sugar. Raw cactus, prickly pear is used in smoothies and fruit salad. This fruit is also used in the making of jam, candy and jellies and in savory dishes like chili. It provides health benefits and it is ideal for losing weight. This fruit is high in Potassium and low in Sodium so it is helpful in preventing high blood pressure. This fruit contains Magnesium, dietary minerals, Calcium and Vitamin C. So it is good for muscle function and bone health. It is also used to treat diabetes, diarrhea, colitis, alcohol hangover, high cholesterol and obesity. They also use it in the treatment of viral infections. The pulp of this plant lowers the level of cholesterol. It is also used to treat cuts, sunburn, bruises and windburn. The pads and fruits of the plant are food for insects, birds and mammals like Javelina (Skunk Pig).

Having discovered a fondness for insects while pursuing her degree in Biology, Randi Jones was quite bugged to know that people usually dismissed these little creatures as “creepy-crawlies”.