Sapindus Saponaria
Scientific Classification
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Genus: | Sapindus |
| Family: | Sapindaceae |
| Order: | Sapindales |
| Species: | S. Saponaria |
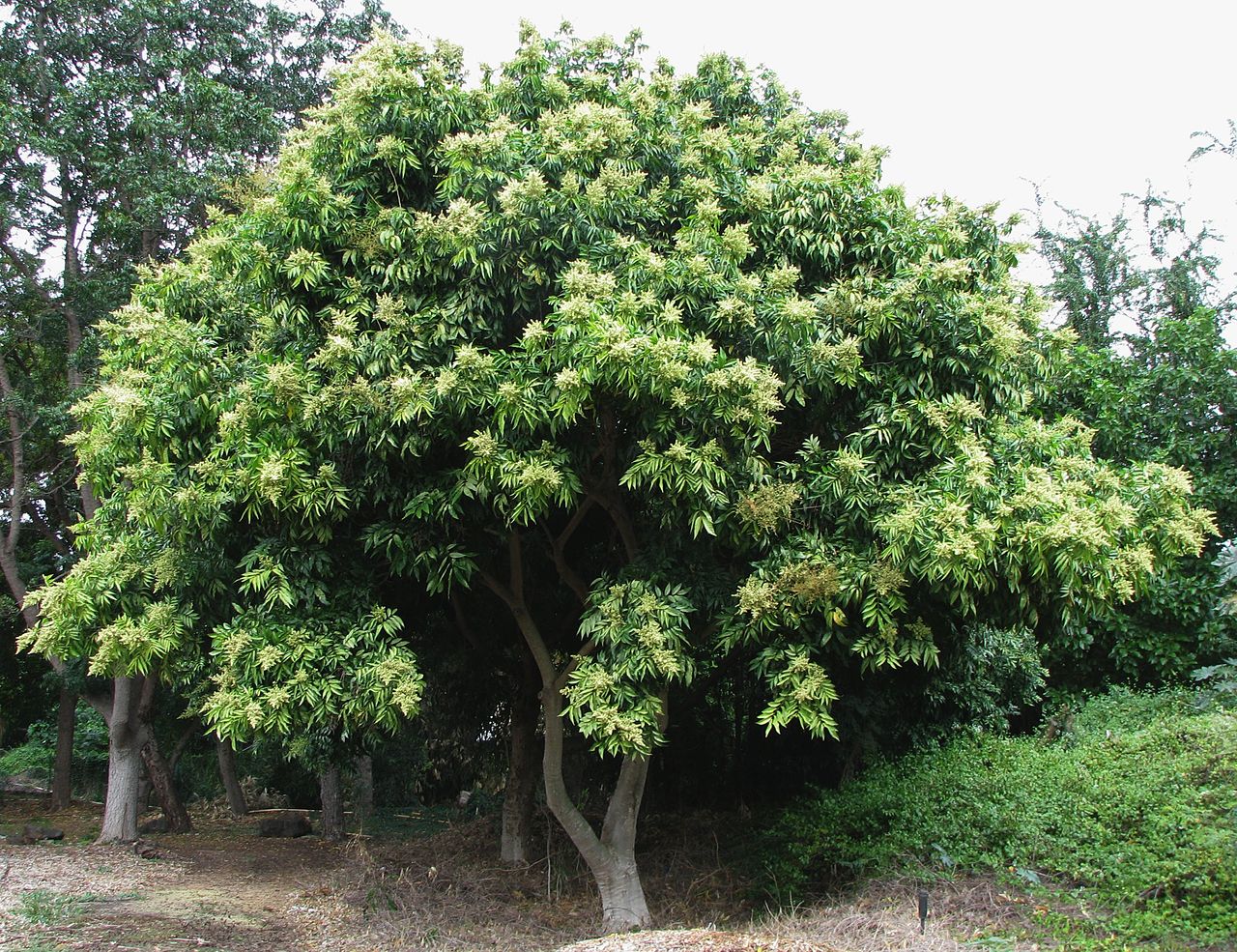
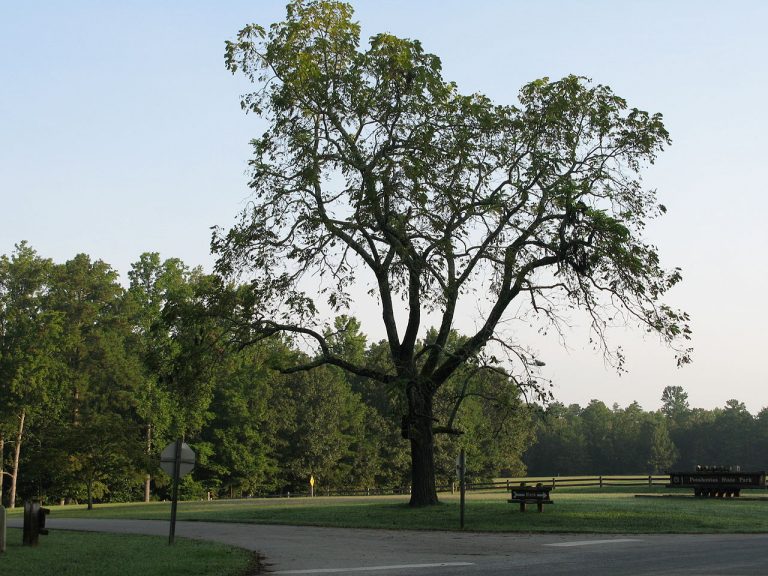
Sapindus Saponaria is a small-sized, deciduous tree. It is also known as Western Soapberry, Wingleaf Soapberry and Manele, Wild China Tree, Cherioni, Drummond Soapberry, Indian Soap Plant, Mexican Soapberry, Cherrion, and Wild China Berry. It can grow up to 50 feet in height. The growth rate of the Sapindus Saponaria tree is medium. It cannot grow rapidly.
The Sapindus Saponaria tree is found on the woodland, rocky hillsides and the edges of the fields. These trees contain soap like substance which is called Saponin, which is a natural detergent that has been used in Mexico as a substitute of soap. And it is used by rubbing the fruit in water. It works like soap. The fragrance of flowers of the Sapindus Saponaria tree attracts many bees, beetles butterflies and moths. The strong and good qualities of the wood of Sapindus Saponaria is a small sized, deciduous tree.
It is also known as Western Soapberry, Wingleaf Soapberry and Manele, Wild China Tree, Cherioni, Drummond Soapberry, Indian Soap Plant, Mexican Soapberry, Cherrion, and Wild China Berry. tree make it resistant to damage by the wind and it is also favorite tree for landscaping. Its shape is rounded and vase shaped. The Jaboncillo blooms in the month of May and June. Male and female flowers of the Jaboncilla tree occur on separate trees. Female trees have a cluster of round and yellowish fruits.
Anatomy
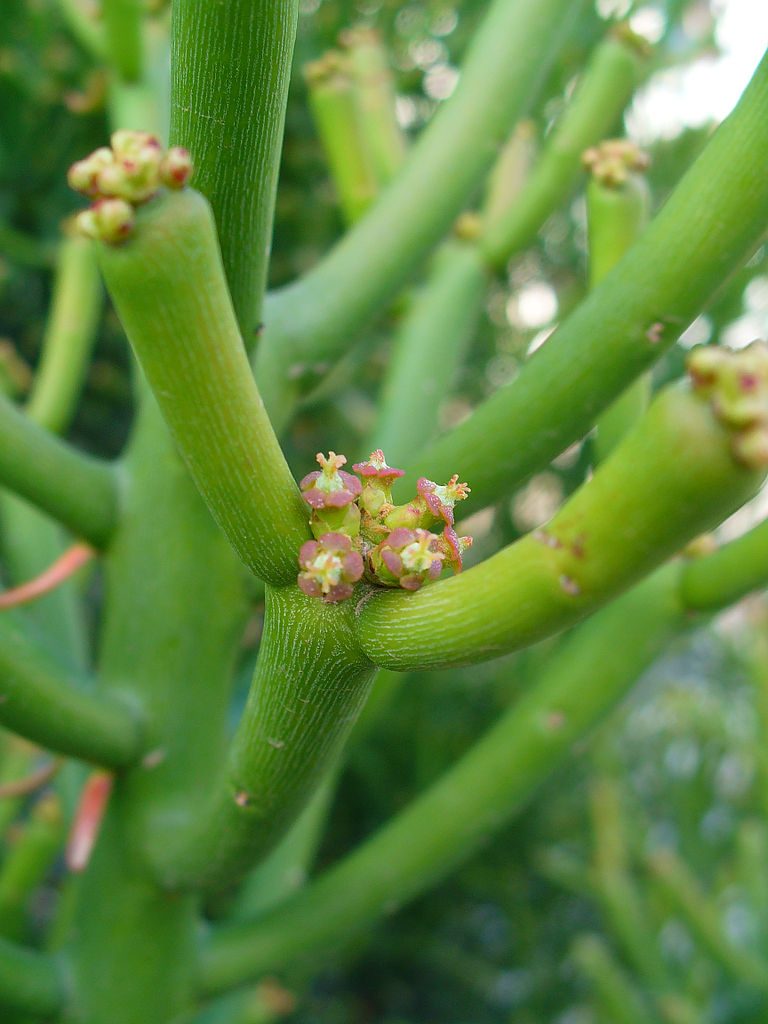
The leaves of the Sapindus Saponaria tree are thick and leathery and pinnately compound. The leaves are deciduous and 20 cm to 38 cm in length. These leaves are made up of 6-20 narrow lanceolate leaflets that have smooth margins. The leaves have uneven wedge shape bases and long tapered tips. At the end of the branches, the fruits occur in the shape of large pyramidal clusters. The fruit is golden in color. And each fruit is 3-3.6 cm in diameter. When the fruit fully matures, it becomes wrinkled and translucent.
The fruit of Sapindus Saponaria contains a single black seed which is about 9 mm in diameter and ripen in the month of October, and till spring they may remain on the tree. The twigs of the Sapindus Saponaria is a small sized, deciduous tree. It is also known as Western Soapberry, Wingleaf Soapberry and Manele, Wild China Tree, Cherioni, Drummond Soapberry, Indian Soap Plant, Mexican Soapberry, Cherrion, and Wild China Berry. tree are gray to brown in color. These twigs are hairy they have short tan colored hair.
But many of them are hairless. Buds are small in size. They are brown in color and are hairless. The trunk is gray to reddish in color. It is scaly. The fruits of Sapindus Saponaria tree are beautiful, but they are not edible because they contain a poisonous substance called Saponin. The fruit of Jaboncilla is inedible and that can be dried and can be stored for further use.
Habitat
The Sapindus Saponaria tree grows from southeastern Colorado to Southwestern Missouri, Texas Eastward, to Louisiana and Mexico, and southward to Arizona. In the moist riparian habitats, it is restricted. These trees have the ability to tolerate drought. The flowers attract bees and butterflies by their attractive shade which turns into dazzling color in the fall. The flowers produce beautiful amber colored berries. It grows naturally along streams, rivers, and creeks. In the Bottomland forest of Oklahoma, Jaboncillo is a very common tree.
Growing at Home

Photo by: Sonoran Desert NPS
Uses
The beautiful berries of this tree are used for making soap. It is not only used as soap, but it is also used in treating kidney problems, fever and rheumatism. The inner bark is also very useful. It is used as an astringent and in the home medical remedies. The wood of this tree is also very useful.
The wood splits into thin strips easily and can be used in the manufacturing boxes, baskets and frames. In the earlier times, the wood was used for making pack saddles, fuel crates and also for cotton basket. Now at times, Sapindus Saponaria (Soapberries) are used as commercial based soap as a substitute of lye. Its sap and seed is also used for medicinal purpose.
Soil
The Sapindus Saponaria tree can grow in moist, well drained and fertile soil. It also grows in clay soil and on dry limestone upland. It can tolerate dry, compacted soil. It requires full sunlight. Full or partial Sunlight is good for ideal growth. They can tolerate wide varieties of soil. It can also tolerate infertile, acidic and alkaline soil very easily.
Watering
These trees require watering daily. This tree can tolerate drought, but for ideal growth of a tree, watering is necessary. In urban conditions, these trees adapt very well. When young, it prefers watering or irrigation regularly.
Pests
Agrilus Prinurus is the serious threat to the Soapberry tree. This borer pest can damage the leaves of the tree. Its nectar is toxic and the fruit is poisonous and it is not used by the wildlife. The fruit is very bitter to eat and may cause stomach ache.

Having discovered a fondness for insects while pursuing her degree in Biology, Randi Jones was quite bugged to know that people usually dismissed these little creatures as “creepy-crawlies”.