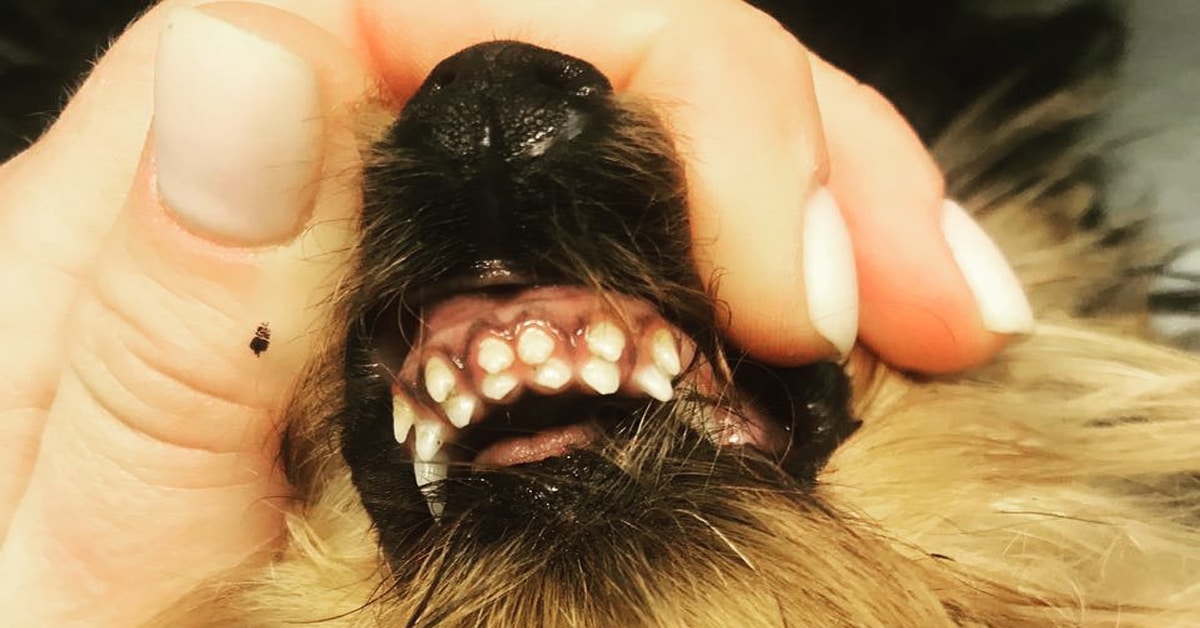
Retained Puppy Teeth – Treatment and Care Tips
A condition known as retained puppy teeth occurs when the permanent tooth emerges. If an adult dog’s retained or prolonged deciduous tooth cannot usually fall out, it may cause oral disorders. Early detection is reliant on you, the owner, and is essential to averting serious harm. A veterinarian should be consulted right away to prevent irreparable harm.
Below, we will explore what retained puppy teeth can cause and how they can be treated.
Teething In Dogs
To see clearly what retained puppy teeth are and why it happens, let’s first learn more about teething in dogs. Adult teeth start to form from tooth buds in the upper and lower jaws long before they emerge through the gums.
The roots of the deciduous teeth are stimulated to start resorbing as the adult teeth start to press on them as they erupt. The crowns of the deciduous teeth erupt after the resorption of the roots. These hollow infant tooth shells may even be found on the ground or in your puppy’s bedding, but they are frequently ingested by puppies when they are eating with no negative consequences.
Your dog may slobber, be reluctant to eat as vigorously as normal, and become agitated owing to a sensitive mouth during the teething phase. The impulse to chew appears in almost every baby dog when teething starts. You should try to steer your puppy’s chewing toward appropriate and secure things. Never let your dog chew on other people’s shoes, clothing, or furniture.
In order to protect your puppies’ teeth, stay away from hard toys, nylon chews, cow hooves, and ice cubes. Avoid giving your puppy any bones, whether cooked or not, since they are difficult to chew and, if ingested, can cause harm to the teeth and intestines.
When Do Retained Puppy Teeth Occur
Dogs experience two sets of teeth during their lifespan, just like people do. Around three weeks of age, puppy teeth, also known as deciduous teeth, begin to erupt, and between four and six months later, an adult set of teeth takes their place. The average dog eventually develops 42 adult teeth, including 10 molars in the far back, 16 premolars in the middle, 4 enormous, sharp canines, and 12 little incisors in the front.
Retained puppy teeth appear when the canine is three to seven months old. The oral problems that develop can be serious and include improper permanent tooth alignment, unintentional bites that could damage the dog’s palate, an aberrant jaw posture, or in extreme situations, the inability to chew without experiencing discomfort. It can be a problem for elderly dogs, although it affects smaller breeds more frequently.
Retained puppy teeth may lead to the eruption of the permanent teeth in unusual places, leading to an unfavorable bite pattern. Similar to the majority of oral health disorders, preventing irreversible damage requires early detection and prompt dental care. Sadly, it frequently stays undetected until much later in life.
Although it can happen in cats, retained deciduous teeth are more prevalent in dogs. Smaller dog breeds, such as the Maltese, Poodle, Yorkshire Terrier, and Pomeranian, are frequently affected.
How To Treat Retained Puppy Teeth
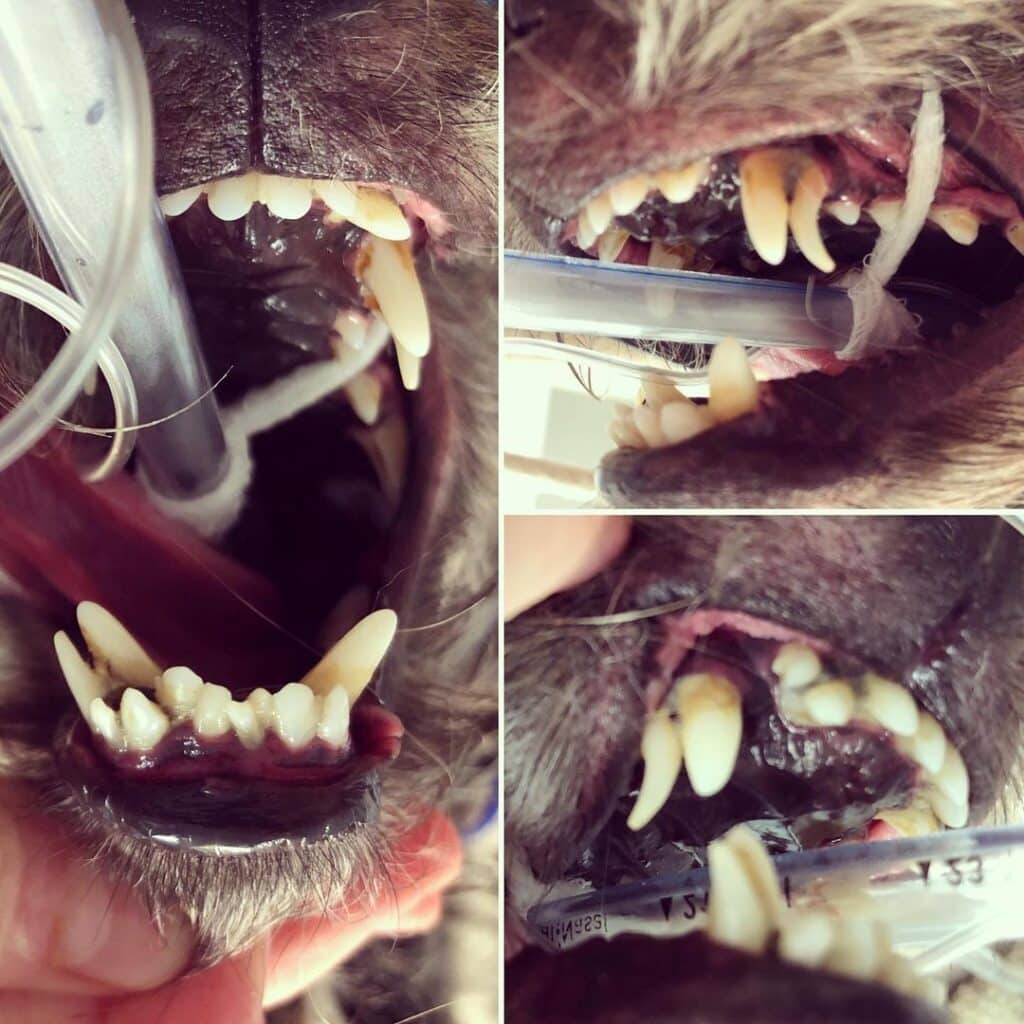
A veterinarian would probably advise having the retained puppy teeth pulled if the deciduous teeth don’t seem to be dropping out on their own. Additionally, retained puppy teeth or fractured teeth may require removal.
While certain dogs may naturally overbite, the tooth extraction procedure is also done to correct that. Long upper jaws are required for breastfeeding, but when a dog ages, the lower jaw should experience a development surge during which adult teeth also erupt. The lower jaw cannot shut correctly if lower teeth are stuck behind higher teeth. A veterinarian can advise removing a few lower baby teeth to fix the problem and allow the jaw to develop properly. Retained puppy teeth, therefore, have to be removed in order to make the room for adult healthy teeth.
A customized plate or tooth shortening may also be helpful, depending on the dog’s teeth, to speed up the process of adult teeth developing properly in the dog’s mouth. Recovery from gum extraction and other gum-related operations should take six to eight weeks. After the extraction procedure, teeth that did not spontaneously erupt within three months should be able to do so within a few weeks.
A feeding tube may be required if a dog has problems swallowing while recovering. It is advised to have regular preventative dental treatment until all of the teeth have properly erupted. Although tooth decay and cavities are very uncommon in dogs, brushing your dog’s teeth twice a day is nevertheless advised.
It is doubtful that the adult teeth will be able to migrate into their normal locations without orthodontic therapy if the stubborn deciduous tooth is not promptly pulled. In these situations, particularly for puppies with significant malocclusion issues, it could be essential to refer your dog to a veterinary dental professional for orthodontic therapy to rearrange the teeth or to selectively extract additional teeth. The use of orthodontic treatment is frequently a part of this treatment.
Cost Of Retained Puppy Teeth Treatment
If tooth extraction is necessary, that will determine the course of therapy for any retained puppy teeth. The typical cost of tooth extraction is $250, but it may cost as much as $1000 depending on the complexity of the procedure, the difficulty of the extraction, and the number of teeth that are about to be removed.
The typical price will be between $312 and $360 if your dog also has his teeth cleaned, as is recommended by the majority of vets while a dental event is taking place.
How To Keep Your Dog Teeth Clean And Healthy
Brushing
Brushing teeth is the cornerstone of excellent oral health for both people and canines. It’s best to clean the dog’s teeth every day. If you are limited in time, cleaning teeth at least once a week would do, however, often the better. Most dogs eventually come to tolerate having their teeth cleaned, even though they initially dislike it.
Dog toothbrushes with specialized handles, soft bristles, and even several heads make it easier and faster to reach all the microscopic, tiny nooks and crevices in your dog’s mouth. You’ll need toothpaste made particularly for dogs because human toothpaste includes potentially harmful toxic components like xylitol and fluoride.
Dog Dental Chews
Dog dental chews assist your dog in cleaning its teeth while also satisfying its natural desire for a tasty reward. Additionally, your dog won’t cause any trouble because he’ll be too busy chewing on treats. These chews are intended to prevent plaque and tartar accumulation while enhancing the shine of a dog’s teeth.
Dog dental chews are available in a variety of sizes and shapes, and they have ridges and nubs that snag in the spaces between a dog’s teeth to promote blood flow through the gums. Dogs can better grasp and chew more evenly because of the hollow forms and voids. Always keep an eye on your dog while they have access to a dental chew.
Dental Sprays
Dog dental sprays are the perfect answer if you don’t have much time to spare or if your dog’s bad breath prevents you from giving him cuddles or kisses. Dog dental sprays may be used either alone or in conjunction with brushing to take care of your dog’s teeth, making it a quick and simple process.
These sprays eliminate plaque-producing germs and freshen your dog’s breath. Along with cleaning and preventing plaque and tartar accumulation, dental sprays also have the added benefit of eliminating smells. The majority of sprays are easy to use, all owners need to do is spritz their dogs’ teeth and gums.
Dental sprays may also be put on dog toys and licked off for immediate fresh breath with little effort, as some dogs just won’t sit still for oral cleaning. The best results are obtained when dogs don’t eat for a half-hour before and after applying dog dental spray.
Regular Professional Cleaning
Regular professional cleanings with your veterinarian are a crucial part of maintaining the dental health of your animal buddy. Veterinarians are skilled in spotting, preventing, and treating oral problems that could otherwise go unnoticed. The majority of dogs require dental examinations and cleanings at least once a year so that vets may look for any early indications of significant issues.
Some breeds, such as Yorkshire terriers, bulldogs, and dachshunds, are more susceptible to periodontal disease than others. Therefore, you might need to clean them more frequently. Veterinarians can remove the plaque below the gum line that toothbrushes can’t reach.
Bottom Line
Retained puppy teeth in dogs are not life-threatening, but they should be extracted as soon as they are noticed. Checking your puppy’s mouth once a week until he is roughly seven to eight months old is crucial in addition to routine tooth cleaning to make sure that his teeth are developing regularly.
Take your puppy to your veterinarian’s office right away for a complete oral examination if you notice any persisting retained puppy teeth or if you have any reason to believe your dog has an unusual bite.

Nato is a content writer and researcher with a background in psychology who’s eager to explore the wonders of nature. As a travel enthusiast and animal lover, she hopes to inspire others to discover and cherish the beauty and importance of the natural world.