Snake Facts
There are a large number of snake varieties in this world. In fact, there are more than Three Thousand kinds of snakes. Pythons, seven or more meters in length are the giants among snakes. They can coil around a full-grown Antelope, squeeze it to death and swallow it without much ado. Then there are pencil-sized tiny snakes. Some snakes inhabit the seas, many burrow underground while others climb and live in trees.
There are venomous and harmless snakes. There are giants and dwarfs. There are deserts, seas, and forest dwellers. However, snakes have a lot of things in common. They are, unblinking, with lidless eyes, long, thin shapes, and legless and scaly bodies. Snakes are reptiles. Like all other reptiles, snakes depend on the sun’s heat to control their body temperature. This is the reason why we find the majority of snake species in the warm and humid tropics.
Snakes are basically very shy creatures. Their habitats, their behavior, their size and adaptations are amazing. Some species of snakes are fast disappearing from the face of the earth. Many more species are becoming extinct. People kill snakes for their skins or because of fear. Their habitats are steadily disturbed, degraded and destroyed by humans. In addition to that, the invasive species that we have introduced are destroying them.
Snake Range
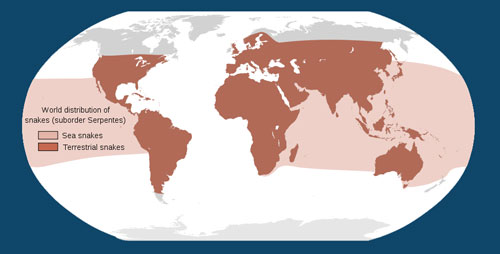
People disturb snake habitats all over the world. It is true that the number of snake species is definitely more in the warm tropics. But snakes are there in every continent except Antarctica. There is one species even in the Arctic circle, which is the adder belonging to the species Viperaberus. Peculiarly enough, there are certain islands that do not have snakes at all. New Zealand, Ireland and Iceland, belong to the group.
Snake Characteristics
Snakes specialized reptiles. They are limbless. Their closest relations are the lizards. Snakes vary greatly in shape, size and length. The variations depend a lot on their lifestyles and diet. We have the teeny ten centimeter snakes to the terrifying ten meter ones. Snakes slither, swim, burrow or climb with ease. Eyesight and hearing are not well developed in snakes. But their other senses more than adequately compensate for those that they lack.
The Peculiar Sensing Tongue
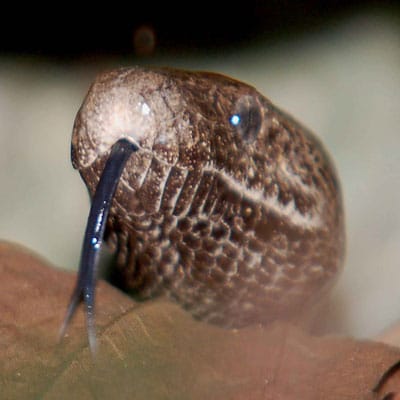

The snakes have the wonderful ability to detect scent molecules. They do this by flicking their tongues. They analyze these scent molecules by a specialized organ named Jacobson’s organ.
Some snake species possess pits in the scales around the mouth. These pits are heat sensitive and these enable them to find out the presence of warm blooded animals.
Shedding Its Skin
Separate scales cover the snake’s skin. A strong keratin layer supports these scales. In course of time the keratin layer gets damaged or worn. This layer does not permit growth also. Snakes have to shed their skin frequently. Shedding of skin is more frequent when they are young. They also shed skin after hibernation. Shedding also happens before and after laying eggs or giving birth. Snakes shed their entire skin, including eye caps, as one piece.
Eating Habits

Snakes are carnivores. They are predators skilled in catching a wide range of prey. Some snakes actively chase and catch their prey. Others lie in ambush to catch the unwary prey. They swallow the smaller prey alive. Poisonous snakes employ venom, while big, non venomous snakes constrict or suffocate their prey to death, before swallowing them.
Snakes have the ability to swallow even very large prey. They have inward curved teeth, lower jaws that are not fused and very flexible skin, which help them to do so. Large prey, they do not have to feed often. Some snakes feed perhaps once a month. Boas and Pythons can subsist for a year without eating.
Venomous Snakes
Snakes are the most feared among reptiles. Only a very small proportion are in fact poisonous. Many of the venomous snakes do not pose any threat to humans. Snakes are not aggressive. They do not bite unless they are threatened. The major portion of snake venom is modified digestive enzymes and juices which help to paralyze or overcome prey It also starts the digestive process by actually aiding in the breaking down of skin and internal organs of the prey.
Breeding
Most snakes are oviparous or egg layers. There are a number of species which give birth to young ones. Many snake species do not provide any parental care. There are certain species like pythons, especially the female pythons that remain with their body coiled around the eggs to protect and incubate them. Snakes reproduce sexually. Some species reproduce by Parthenogenesis, which means hatching from unfertilized eggs, since the members of the species are all females. A typical example is the Brahminy (blind) snake.
Interesting Facts About Snakes

- Of more than 3,000 snake species, only 375 species are poisonous. Only a very small percentage of these can be harmful to human beings.
- There are no vegetarian snakes. All of them are carnivores.
- Snakes do not possess external ears or eye lids.
- The inland Taipan, with its extremely toxic venom, is considered to be the world’s deadliest snake. The quantity of venom in a single bite has the potential to kill 100 humans. Funnily, no human till now has died of Taipan bite.
- The reticulated python is the longest living snake. It can reach more than ten meters in length.
- The longest snake ever is said to have lived over 60 million years back. The Titan boa could have been more than 15 meters in length.
- The Barbados thread snake is the world’s smallest snake. The species that was discovered in 2008, was just 4 inches long.
- The Gaboon viper has longest fangs in snakes. The fangs are around fifty millimeters in length.
- The world’s fastest snake is the Black Mamba. It can move at 20 kilometers per hour.
- Spitting cobras spit venom up to a distance of 8 feet with the help of their modified fangs.
- The only creatures in the world, with similar binomial and scientific names, are the Boa Constrictors.
Conclusion
All over the world, the biggest threat that the snake faces is habitat loss. The fast expanding human populations require additional resources and space. The introduction of invasive predatory species has disastrous consequences for snakes. Snakes are killed for their skins and meat. They are also collected for the pet trade. Snakes are also killed by the local people out of fear.
One must adopt a number of measures to conserve snakes. The creation of National parks, Nature Reserves and Awareness Programs to educate people to overcome their prejudice towards snakes, can all help in this process. Breeding snakes in captivity is a good option for this, but only a limited one.

Having discovered a fondness for insects while pursuing her degree in Biology, Randi Jones was quite bugged to know that people usually dismissed these little creatures as “creepy-crawlies”.







