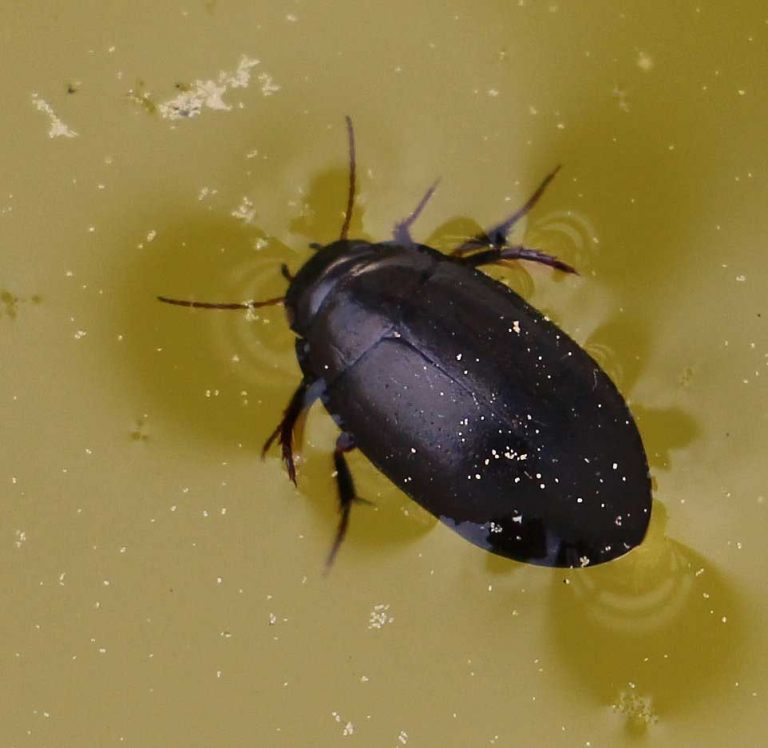
Dermestid Beetle
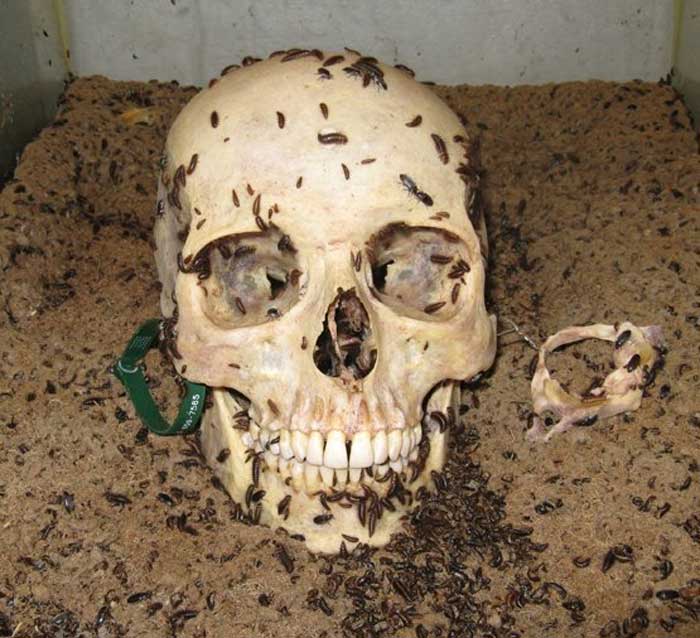
A Human Skull Being Cleaned by Dermestid Beetles
Scientific Classification
| Kingdom: | Animalia (Animals) |
| Phylum: | Arthropoda (Arthropods) |
| Subphylum: | Hexapoda (Hexapods) |
| Class: | Insecta (Insects) |
| Order: | Coleoptera (Beetles) |
| Suborder: | Polyphaga (Water, Rove, Scarab, Long-horned, Leaf and Snout Beetles) |
| Superfamily: | Bostrichoidea (Carpet, Powder-post and Death-watch Beetles) |
| Family: | Dermestidae (Carpet Beetles) |
Launching
Scientific records estimate that there are about five hundred to seven hundred kinds of Dermestid beetles throughout this universe. They belong to the category of Dermestidae and exist in the scientific order, of Coleoptera. They have a number of names and the most accepted one is Skin Beetles, the others being Larder Beetles, Leather Beetles, Carpet Beetles, and Khapra Beetles. Their length varies from 1mm to 12mm. One of the distinguishing traits of the adults is that their spherical, or rather elliptical outer structure is camouflaged with bristles or hair-like structures. Even their larvae have this feature. Their antennae are fitted deep inside their head. The posterior thigh bone is appropriately fixed in the hip joint.
The genus consisting of Dermestids feed mainly on decaying matter such as carcasses or things belonging to the vegetable kingdom like the fine granular substance in flowers and also the thin strands. The Dermestes reside in the body of decaying animals, whereas others can be seen in beasts, fowls and bees.
Two varieties of species are Thaumaglossa, which reside only in the egg sheaths of Mantids, and Trogoderma, which are very much harmful to the crops.
Some are very much helpful like the beetles having connection with the decaying corpse. They are important in forensic etymology. On the other hand, some create a disturbance by destroying the vegetation.
Physique
Matured beetles are egg shaped and are shorter in physical measurement. Most probably, they have a deformed aerial. Some categories have colorful bristles throughout their external parts. The length varies from 1/16 inch, as seen in the varied carpet beetle, to 3/8 inches like that of larder and hide beetles.
Larvae of Dermestid Beetles acquire a v–shape, by tapering towards a point, shielded with fine strands of hair and some will have a long collection of hair towards the posterior part. Most probably they are not more than ½ inch long, though its measurement is calculated differently according to the respective categories.
Life Process
Duration of the wheel of life differ much in Dermestids. Some groups hatch out of the eggs and become mature within six weeks whereas some other categories attain total maturity in one year or further. Dermestids have four stages in life with which they are subjected to entire transformation, namely, egg, larvae, pupa, and adult.
Females select fissures or concealed places to place their eggs. The larvae molt in sixteen phases, and thereafter, succeeding the pupal stage, mature ones come up prepared for copulation.
Providing Nourishment
Some of the Dermestid larvae have their own choices in the case of food. A few of them enlarged their eating habits to herbal proteins, granulated things, cereals, nuts, and spiceries. A group of them go to the extent of eating fabrics and cotton.
The Dermestids nibble on cashmere attires, Quilts, and nappy floor coverings, thus make small cavities in it as they are able to assimilate fur and other fibrous materials. Carpet beetles, while comparing with the insects that cause harm to the clothes, do much detriment to the flannels and may sometimes cause its total destruction. Clothes moths are a major problem in states having high humidity.
Most probably the larva or the outer layer of the old skin can be seen generally in the bed-chamber where the fur gets collected and also all over the couch or in the wardrobe in which the flannel apparels are stocked. High chances exist for them to be detected in places where our tamed animals slumber as these Dermestids devour the beautiful fur of our beloved pets and it becomes a grave problem when people have small trained animals that are staying inside the home.
Proliferation
In all the moderately hot conditions, the Dermestid Beetle community procreates without any pause. It is necessary to give nourishments, as well as, sufficient moisture-less substratum and heat for the proper development of the beetles. Their embryos are very minute and one may fail to perceive it with the naked eyes. These miniature larvae will start taking food as soon as they emerge out from the egg. They ingest greater amount of meat. Larvae cast off their Dermis as they become bigger. On extending up to 10mm to 12mm, the larvae transform into the pupal stage. In this phase, most of the time, they wait within the substrate and make their appearance outside only to take food.
As a Destructive Force
As said earlier, some of these beetles are very helpful, whereas some others are destructive as they act as pests thereby demolishing our vegetation. In order to keep all items away from the Carpet beetles, make sure that all the items are pest–free and also tidy. Keep them in airtight vessels and place layers of paper every few inches inside.
Either small pellets of naphthalene, sliver or stimulants that include Para dichlorobenzene (PDB), also termed as 1,4-Dichlorobenzene, can be utilized, to get mastery over the carpet beetles, on clothes or you can use soaked defoliant resin layers which can be applied on the indicated strata of papers. Be very cautious that kids and pets are not able to get on to these things; likewise prevent applying these substances in places where you store edible things and prevent them to get in touch with eatables or baking vessels. Utmost care has to be taken in avoiding these beetles or their larvae accessing knobs made of synthetic materials, hangers or costume pouches because the active components may soften the plastic and cause it to melt into the clothes.
One has to make sure that these commodities are branded for applying indoors. Layers of resins give longer influence than PDB and are usually of greater power in safeguarding exposed articles in confined bags, as they consist of Dichlorovos (DDVP) as the basic ingredient. Avoid using resin strips in places where people stay for longer periods of time. On evaporation, these chemicals in adequate concentration will vaporize and destroy the insects slowly. The vapors will be made in necessary concentration only for airtight vessels. Suppose the vessel containing these elements are not sealed properly, fully grown up ones will be driven off, but the larvae which exists there earlier may carry on the process of eating the stuff.
A mature Dermestid Beetle aids in enhancing the community of Dermestids at a high rate, particularly, the ovum carrying females. If anyone is interested in keeping these beetles, confirm first that the source community contains Dermestids in different phases of development, containing very small, intermediate, and big larvae, pupae and fully grown up beetles.
New hobbyists have a misunderstanding only a few hundred beetles are sufficient to start cleaning the skulls. It is a fact that we can start cleaning the skulls of tiny mice and rodents with a few hundred bugs, but in order to clean larger skulls like that of bear, deer and boar, you must have thousands of beetle larvae as they do most of the work.
It is better to buy some egg laying females to build up the community. Also care must be taken in selecting the right group of Dermestid Beetle. Starch favoring Dermestes are called “pantry beetles”. Commonly, people used to sell the protein eating category termed as Dermestes Maculatus to clean the flesh.
It requires little effort for the Dermestid Maculatus group to flourish as their transformation process will be fully over within thirty days in desirable conditions. Females produce about three hundred ovums throughout her life.

Having discovered a fondness for insects while pursuing her degree in Biology, Randi Jones was quite bugged to know that people usually dismissed these little creatures as “creepy-crawlies”.